Please update your browser
We have detected that you are using an outdated browser that will prevent you from using
certain features. An update is required to improve your browsing experience.

We have detected that you are using an outdated browser that will prevent you from using
certain features. An update is required to improve your browsing experience.
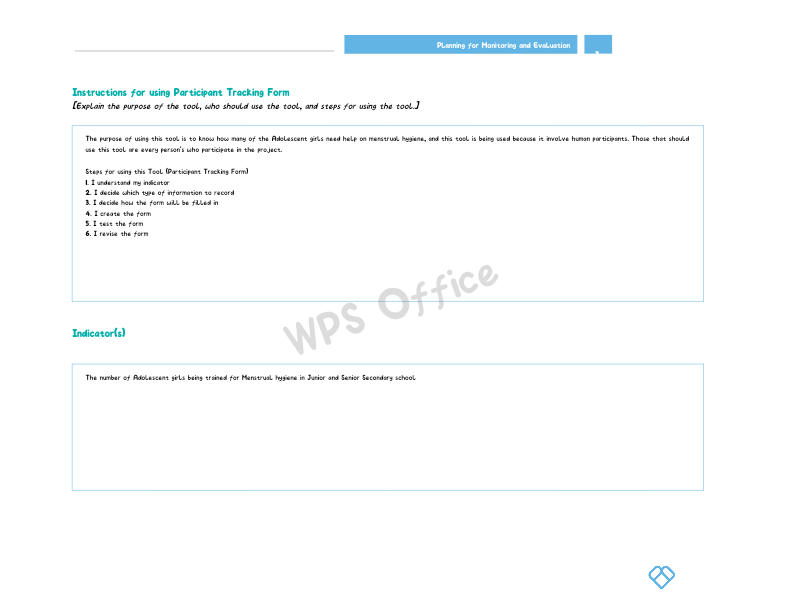
Data Collection Tools: Instruments, methods, or procedures designed to systematically collect data for research, monitoring, or evaluation purposes. These tools can include surveys, questionnaires, interviews, observations, and other means of gathering information from individuals or sources.
this is one of major role in project management, i think tracking form is the cheapest way for data collection thou its not safe and the information can be forged
i think meh could`ve also added observation method to track down its participant
its not mandatory some projects they do not need a tracking form,, you may use different kinds of methods depending on the nature of your project or indicators of the projects
yes because it determine what kind of a tool you gonna need for your data collection
Considering the knowledge I have acquired from this course, creating data collection tools is crucial in Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) as it ensures the systematic and standardized gathering of information, enabling accurate measurement and evaluation of program outcomes. A well-designed tool can contribute to the reliability and validity of collected data, providing a foundation for informed decision-making and program improvement in the context of M&E.
Every data collection tool has own advantages and drawbacks. Choosing appropriate data collection tool is important to monitor and evaluate the project outcomes through indicator that you have created. Also, instruction of data collection should be ver clear for data collector.
Every data collection tool has own advantages and drawbacks. Choosing appropriate data collection tool is important to monitor and evaluate the project outcomes through indicator that you have created. Also, instruction of data collection should be ver clear for data collector.
Data Collection Method: Data for these indicators are collected using the same method: interview, survey, etc.
Source: Data for these indicators come from the same source: a group of people, a place, an environmental feature, etc.
Collection Schedule: Data for these indicators are collected on the same schedule: weekly, monthly, annually, etc.
A data collection tool is a mechanism or instrument used to gather information or data from individuals, groups, or systems for research, analysis, or decision-making purposes. It can take various forms depending on the nature of the data being collected and the methodology employed. Here are some examples of data collection tools:
Surveys: Surveys involve asking questions to gather information from respondents. They can be conducted in various formats such as online surveys, paper surveys, telephone surveys, or face-to-face interviews.
Questionnaires: Questionnaires are structured sets of questions designed to gather specific information from respondents. They can be administered in written or electronic formats and can be used for quantitative or qualitative data collection.
Interviews: Interviews involve direct interaction between an interviewer and a respondent to gather information. They can be structured (with predefined questions), semi-structured (with a mix of predefined and open-ended questions), or unstructured (free-flowing conversation).
Observations: Observations involve systematically watching and recording behaviors, events, or phenomena in their natural settings. Observational data collection can be done through field notes, checklists, or video/audio recordings.
Focus Groups: Focus groups involve bringing together a small group of people to discuss a specific topic or issue. They are often used to gather qualitative data and insights through group discussions and interactions.
BELOW ARE DESIGN TIPS TO USE WHEN CREATING THE DATA COLLECTION TOOL;
I have gained valuable insights from Module 4 regarding data collection tools and the step-by-step process of developing data collection methods. This module has taught me the importance of selecting the appropriate data collection methods such as surveys, focus group discussions (FGDs), observations, and interviews. I now have a better understanding of how to choose the right method based on the research objectives and the type of data needed. Overall, this module has provided me with practical knowledge on effectively collecting data for research purposes.
Creating data collection tools is one ways which can lead to a successful project when it is conducted and collected correctly.
They're few questions to be asked when collecting the data such as when why and when
Age and location of the people involved in a project .
This helps how the project can be evaluated in future
Either it was successful or not data is very important
Data Collection Method: Data for these indicators are collected using the same method: interview, survey, etc.
Source: Data for these indicators come from the same source: a group of people, a place, an environmental feature, etc.
Collection Schedule: Data for these indicators are collected on the same schedule: weekly, monthly, annually, etc.
M&E starts with good project design. Before you can make an M&E plan, you need to really understand your project’s activities and intended effects.
A logframe is a project design tool. It brings together lots of important information into one place. Completing a logframe is one of the first steps in the project cycle.
The project summary should have a logical flow. Each level should logically lead to the level above it. Whenever possible, you should find evidence to support your logical flow.
It is very important to identify risks and assumptions before a project starts. If you know how a project might go wrong, you can start preparing. You will also know what problems to look for when you start monitoring.
Data Collection Method: Data for these indicators are collected using the same method: interview, survey, etc.
Source: Data for these indicators come from the same source: a group of people, a place, an environmental feature, etc.
Collection Schedule: Data for these indicators are collected on the same schedule: weekly, monthly, annually, etc.
It's important to understand the sort of data a monitoring or evaluation exercise is seeking in order to choose the most appropriate tools. Some tools may cost time, money and effort only to fail to meet the requirements of the exercise. In this case, the pilot studies are very helpful as they help detect these issues before full deployment of the tools
The steps in creating a Data Collecting Tools are really insightful. It is indeed important to consider all the tips so as to have a good tool that will get accurate data.
for creating data tools, I have learned there are different tips to considering .
1)identify who will use this tool
2)focus on ESSENETIAL information
3)collect metadata
A strong Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) plan requires the development of efficient Data Collection Tools. These instruments form the foundation for obtaining precise and trustworthy data, facilitating well-informed decision-making. Designing tools that are in line with project goals is essential to making sure they effectively gather pertinent data. Pilot testing and incorporating stakeholder feedback can improve the efficacy of the instrument and promote thorough data collection procedures.
To determine the most suitable data collection tool for your project aimed at providing access to clean water for people in Rusizi, consider the following options:
Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys and questionnaires can be used to gather information from community members about their current water access, sanitation practices, and preferences for improvements. This method allows for collecting both quantitative and qualitative data, including demographic information, water usage patterns, and community perceptions.
Creating tools looks straightforward especially the participant tracking form. It however is not the case for the other tools, even existing ones because it entails filling it to the project using imagination and then testing it may end up being disappointing.
The steps in creating a Data Collecting Tools are really insightful. It is indeed important to consider all the tips so as to have a good tool that will get accurate data.
How does SOFT skills influence the effectiveness of data collection?
Data collection tools are created when there is no existing tool to effectively collect the type of data you want to record.
It is always important to test the tool that has been created in order to identify its effectiveness and whether there's errors that need revised.
Training on how to use the created tool is required. The people to use the tool are unfamiliar with the tool created, making it hard for them to use it as required, hence training is required.
When Creating data Collection tools, one should consider the type of data to be collected, the person collecting, date and day of collection and the participants age, gender and the Area
When Creating data Collection tools, one should consider the type of data to be collected, the person collecting, date and day of collection and the participants age, gender and the Area
Creating data collection tools involves several steps to ensure that the tools effectively gather the necessary information. Below is an outline of the key steps in creating data collection tools:
Define the Purpose:
Clearly define the objectives and research questions that the data collection tools will address.
Determine what specific data needs to be collected to achieve the research goals.
Select Data Collection Methods:
Choose the appropriate data collection methods based on the research objectives, available resources, and target population.
Common methods include surveys, interviews, observations, document reviews, and existing data analysis.
Design the Structure:
Determine the structure and format of the data collection tool, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or observation checklists.
Decide on the layout, including the sequence of questions, response options, and any instructions or prompts.
Develop Questions:
Create clear, concise, and unbiased questions that address the research objectives.
Use language that is appropriate for the target audience and ensure that questions are easy to understand.
Avoid leading or loaded questions that may bias responses.
Pretest the Tool:
Conduct a pilot test or pretest of the data collection tool with a small sample of participants.
Evaluate the clarity, comprehensibility, and relevance of the questions.
Identify any ambiguities, errors, or problems with the tool and make necessary revisions.
Finalize the Tool:
Incorporate feedback from the pretest to refine and finalize the data collection tool.
Ensure that the tool is comprehensive, reliable, and valid for collecting the desired data.
Double-check the formatting and layout to ensure clarity and professionalism.
Train Data Collectors:
Provide training to data collectors on how to administer the data collection tool consistently and accurately.
Ensure that data collectors understand the purpose of the research, ethical considerations, and confidentiality protocols.
Implement Data Collection:
Implement the data collection process according to the established protocols and timeline.
Monitor data collection activities to ensure quality control and adherence to procedures.
Address any issues or challenges that arise during data collection promptly.
Analyze and Interpret Data:
After data collection is complete, analyze the collected data using appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis techniques.
Interpret the findings in relation to the research objectives and draw conclusions based on the data analysis.
Disseminate Results:
Present the findings of the data analysis in a clear and accessible format, such as reports, presentations, or publications.
Share the results with relevant stakeholders and decision-makers to inform policy, programs, or further research efforts.
By following these steps, organizations can develop effective data collection tools that generate reliable and valid data to support their research objectives.
Creating data collection tools
Give tittle
Purpose of the form
Provide estimate of time needed
Provide clear instructions and information needed
Great contributions
Great contributions
Sometimes it is possible to use a data collection tool that has already been created if you are measuring an indicator that other projects have already used., it is worth investigating whether an appropriate tool already exists. Using a pre-existing tool can save a lot of time and resources, and this can ensure that the tool you use is high quality.
When creating data collection tools, firstly, you need to identify who will use the tool in collecting data as this will help you have a clearer idea of how to design your tool. Secondly, you need to focus on collecting essential information, these are the data that you need to measure your indicators, so it doesn't get too complicated. Thirdly, you have to collect metadata, this explains how your data was collected. Fourthly, you need to pre-test your tool, if possible, especially in the same environment that it will eventually be used in, this will help you notice if there is any error with your tool and make a revision or not. Lastly the handlers of the tools have to be trained and instructions be included on how to use the tool as this saves you from the assumption that your tool is self-expalnatory and having to collect inaccurate data.
ata management focuses on capturing, validating, storing, and protecting data. Besides that, a lot of effort goes into processing the data to ensure its quality and reliability. Big data is becoming increasingly important for organizations to make more data-driven decisions. This data helps organizations understand their customers, spot new trends, improve their existing services, and even develop new services.
The data collection tools discussed in this topic are very clear. Specifically, the use of a participant tracking form has proved to be the best methods for one of my current projects.
NOTABLE AREARS IN CREATING DATA COLLECTING TOOLS
When creating data collection tools, there are several key notable areas to consider. Here are some important aspects to keep in mind:
Clarity and Simplicity: Ensure that the data collection tools are clear and easy to understand for both the data collectors and the participants. Use simple language and avoid jargon or technical terms that may confuse or intimidate the participants.
Relevance and Validity: Include questions or fields that are directly related to the indicators you are measuring and the goals of your project. Ensure that the data collected will provide valid and meaningful insights.
Standardization: Maintain consistency in the format and structure of the data collection tools. This will help in data analysis and comparison across different participants or time periods.
Data Types: Determine the types of data you need to collect, such as numerical data (age, number of attendees) or categorical data (satisfaction levels, eye conditions). Design the tools accordingly to capture the appropriate data types.
Practicality and Feasibility: Consider the practicality and feasibility of the data collection tools in the context of your project. Ensure that they can be easily administered, completed, and processed within the available resources and time frame.
Ethical Considerations: Respect ethical guidelines and ensure the privacy and confidentiality of the participants' data. Obtain informed consent when necessary, and clearly communicate how the data will be used and protected.
Piloting and Testing: Before implementing the data collection tools on a large scale, conduct a pilot test to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Gather feedback from data collectors and participants to refine the tools as needed.
Training and Guidance: Provide training and clear instructions to data collectors to ensure consistent and accurate data collection. Clarify any questions or concerns they may have, and establish a communication channel for ongoing support.
Data Management: Plan how the collected data will be stored, managed, and protected. Establish a system for data entry, organization, and backup to ensure the integrity and security of the data.
Data Analysis and Reporting: Consider how the collected data will be analyzed and reported. Determine the appropriate analysis methods and reporting formats to effectively communicate the findings of your project.
By paying attention to these notable areas, you can create effective data collection tools that will enable you to gather accurate and relevant information for your project.
NOTABLE AREARS IN CREATING DATA COLLECTING TOOLS
When creating data collection tools, there are several key notable areas to consider. Here are some important aspects to keep in mind:
Clarity and Simplicity: Ensure that the data collection tools are clear and easy to understand for both the data collectors and the participants. Use simple language and avoid jargon or technical terms that may confuse or intimidate the participants.
Relevance and Validity: Include questions or fields that are directly related to the indicators you are measuring and the goals of your project. Ensure that the data collected will provide valid and meaningful insights.
Standardization: Maintain consistency in the format and structure of the data collection tools. This will help in data analysis and comparison across different participants or time periods.
Data Types: Determine the types of data you need to collect, such as numerical data (age, number of attendees) or categorical data (satisfaction levels, eye conditions). Design the tools accordingly to capture the appropriate data types.
Practicality and Feasibility: Consider the practicality and feasibility of the data collection tools in the context of your project. Ensure that they can be easily administered, completed, and processed within the available resources and time frame.
Ethical Considerations: Respect ethical guidelines and ensure the privacy and confidentiality of the participants' data. Obtain informed consent when necessary, and clearly communicate how the data will be used and protected.
Piloting and Testing: Before implementing the data collection tools on a large scale, conduct a pilot test to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Gather feedback from data collectors and participants to refine the tools as needed.
Training and Guidance: Provide training and clear instructions to data collectors to ensure consistent and accurate data collection. Clarify any questions or concerns they may have, and establish a communication channel for ongoing support.
Data Management: Plan how the collected data will be stored, managed, and protected. Establish a system for data entry, organization, and backup to ensure the integrity and security of the data.
Data Analysis and Reporting: Consider how the collected data will be analyzed and reported. Determine the appropriate analysis methods and reporting formats to effectively communicate the findings of your project.
By paying attention to these notable areas, you can create effective data collection tools that will enable you to gather accurate and relevant information for your project.
A well designed form yields to quality results. Once it's detailed, it'll inform the project about required information.
Creating data collection tools in a project design for Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) involves several key steps:
Your data collection and data management processes will be complicated systems that involve many people. In complicated systems like this, it is easy to make mistakes. One way to avoid mistakes in complex systems is to very carefully describe what each person is responsible for doing. This ensures that everyone understands their role in the project, that there is no confusion over who is responsible for each task, and that no important task is forgotten.
ata collection methods are essential for gathering information effectively and efficiently. With numerous methods at our disposal, it is crucial to understand each method's strengths and weaknesses to choose the most appropriate one for the task at hand. While some methods require specialized knowledge, others are user-friendly and can be managed by trained individuals. Moreover, certain methods can be more time-consuming and costly than others, and it's important to weigh these factors when selecting a method. Depending on the type of data needed, some methods may be more effective than others. By understanding and utilizing various data collection methods such as surveys, interviews, group discussions, observations, and document reviews, we can gather valuable information that can inform decision-making and improve outcomes.
We should consider these questions in date collection method:
• What- What kind of data do we need?
• Who- Who will provide data?
• How often- How often should we collect data?
• By whom- who will collect the data?
• Can we do it-do we have enough time and resources to collect data?
Someone has to be mindful of the kind of data in question so that right tools are used for data collection. Being mindful of the indicators will assist in coming up with right tools
Very true. Trainings of the participants being involved in the data collection is very important as they familiarize themselves with the questions and and make necessary inputs
Well designed data collection tools are essential for any analysis hence a need to be mindful of choosing a right tool that corresponds to the kind of data needed and required for any project
Great contributions
This module is really insightful, this example mainly focuses on survey as data collection methods but neglected other forms such as focus group, observation, etc.
My question is how would MEH use focus group, interview and observation to complement their data collected.
Enjoy Learning and Playing using URUKUNDO Life Skills BOARD GAME
Data collection tools are devices used to collect data such as paper questionnaires, computer-assisted interviewing systems, checklists, interviews, surveys, and observation sometimes. When creating a data collection tool you should identify who will use the tool, and their expertise, focus on essential information ,collect metadata, pretest your tool, test the staff to use the tool and include instructions.
It is always great to create a data collection tool for your project as it helps to keep track of your progress. It helps you focus on the important things that you need for your business and also make great tools for data collection.
it's important to ensure that data collection methods are aligned with the objectives of the evaluation, the characteristics of the target population, and ethical considerations. Additionally, data quality assurance measures, such as training data collectors, piloting instruments, and ensuring data validity and reliability, are essential to produce reliable and credible findings.
Overall, effective data collection is essential for generating evidence-based insights that inform decision-making, improve program effectiveness, and drive positive change in development initiatives.
There are various methods of data collection in M&E, including:
Surveys and Questionnaires: Surveys involve gathering data from a sample of individuals or organizations through structured questionnaires. This method is useful for collecting quantitative data on a wide range of topics.
Interviews: Interviews involve direct conversations with individuals or key informants to gather detailed qualitative data. They provide an opportunity to explore perspectives, experiences, and opinions in depth.
Focus Group Discussions (FGDs): FGDs bring together a small group of individuals to discuss specific topics in a structured setting. They are useful for exploring shared experiences, perceptions, and attitudes within a community.
Document Reviews: Document reviews involve analyzing existing records, reports, and documents related to the project or program. This method provides valuable insights into past activities, achievements, and challenges.
Observations: Observations involve directly observing activities, processes, or events to gather real-time data. This method is particularly useful for assessing behaviors, practices, and conditions in a natural setting.
Quantitative and Qualitative Data Analysis: Once data is collected, it needs to be analyzed. Quantitative data is typically analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. Qualitative data is analyzed thematically to identify recurring themes, insights, and interpretations.
Data tools should be carefully designed in a manner that it collects the correct informations to addresses the indicators it is meant to achieve while also considering who the user of the tool will be. The tool should also collect metadata, contain necessary instructions, must have being pretested to correct all necessary errors and finally must have been used to train who will be using it.
From what I have learnt in this module, creating data collection tools helps you keep your focus on the essential data needed for your project. It zeroes in on the core use of indicators and how they can be measured clearly with almost no room for errors. Creating a data collection tool is a great way to test your indicators and see if they are best suited for project's goals.
To create data collection tools, you need to know the following steps
1- you need to know who use this tool
2-you also need to focus on important information that will clear definition about what need to be collected
3- you need to collect metadata in addition to vital information
4-you need to pre test you tool to know its effectivesness
5- final you need to train the data collectors who willbe deployed to collect the data
When you understand your indicator , it paves way for what kind of data you will be collecting. The data could be quantitative or qualitative. From this stage, you will have to select the method for collecting the data. It could be using a survey, interview or focus group. Once you know this identify indicators which can fall under the same data collection method for the same beneficiaries and develop a tool. Make sure the tool is tailored for those who will collect the data and collect it from in respect to the information you need
Très importante partie.
Its very important when creating data collection tools to look critically into the five tips discussed in this session, this wiil ensure the data collected is accrurate and consistent and that it will be essential for measuring the defined indicator.
Use of simple and understandable language and pretest of your tool helps to redifine and revise your tool ,to avoid any ambiquity.The steps for creating a tool as learnt are:
Creating data collection tools can take a significant amount of time and I think it is often underestimated how much time and effort needs to go into developing good data collection tools. It is critical to pilot and revise data collection tool, in our case we did two rounds of revisions: one after getting feedback from the trainers and a second time after receiving feedback from participants.
the Key take home messages i have learnt are that
Questionários e Entrevistas: Desenvolver questionários estruturados para os pais ou responsáveis das crianças pode ajudar a coletar informações sobre hábitos alimentares, acesso a alimentos, práticas de amamentação, conhecimento sobre nutrição infantil, entre outros aspectos relevantes.
Registros de Saúde: Utilizar registros de saúde infantil para coletar dados antropométricos, como peso, altura/comprimento e circunferência da cabeça, ao longo do tempo. Esses registros também podem incluir informações sobre o histórico de saúde da criança e intervenções nutricionais.
Observação Direta: Realizar observações diretas em clínicas de saúde, creches ou comunidades para avaliar o ambiente alimentar das crianças, comportamentos alimentares e práticas de cuidados infantis.
Testes Biomédicos e de Laboratório: Quando apropriado e viável, realizar testes biomédicos para avaliar o estado nutricional das crianças, como testes de deficiência de nutrientes específicos ou exames de sangue.
Grupos Focais: Organizar grupos focais com pais, cuidadores e profissionais de saúde para explorar percepções, conhecimentos e experiências relacionadas à nutrição infantil e identificar possíveis barreiras e soluções para melhorar a saúde nutricional das crianças.
Monitoramento de Indicadores de Desnutrição: Estabelecer indicadores claros de desnutrição, como taxa de desnutrição aguda ou crônica, taxa de baixo peso ao nascer, taxa de aleitamento materno exclusivo, entre outros, e coletar regularmente dados sobre esses indicadores para avaliar o progresso do programa.
Avaliação de Programas Existentes: Caso existam programas de nutrição infantil em vigor na região, é importante avaliar sua eficácia por meio de dados quantitativos e qualitativos para identificar áreas de sucesso e oportunidades de melhoria
Dados físicos: Puedes adquirir dados en tiendas de juegos o en línea. Vienen en una variedad de formas y tamaños, desde el tradicional dado de seis caras hasta dados de formas más exóticas y con más caras.
Aplicaciones móviles: Hay muchas aplicaciones gratuitas disponibles para dispositivos móviles que simulan el lanzamiento de dados. Pueden ser útiles si no tienes dados físicos a mano.
Sitios web: También hay sitios web que ofrecen servicios de lanzamiento de dados en línea. Algunos incluso permiten personalizar el tipo de dado que quieres lanzar.
Software de juegos de mesa digital: Si estás interesado en juegos de mesa digitales, hay software y aplicaciones que te permiten jugar juegos de mesa en línea, incluyendo el lanzamiento de dados.
Creating data collection tools can take a significant amount of time and I think it is often underestimated how much time and effort needs to go into developing good data collection tools. It is critical to pilot and revise data collection tool, in our case we did two rounds of revisions: one after getting feedback from the trainers and a second time after receiving feedback from participants.
Creating data collection tools in Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) involves designing instruments or forms that facilitate the systematic gathering of relevant information to assess the progress and impact of a project or program.
Creating data collection tools in Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) involves designing instruments or forms that facilitate the systematic gathering of relevant information to assess the progress and impact of a project or program.
Effective data collecting is crucial regardless of your subject of study—development economics, international development, nonprofit organizations, or any number of other businesses. It improves decision-making and expands the influence of your company. But gathering data can be a difficult and complicated task.
It is important to identify who will use the tool, focus on essential information, such as participants gender, location, education level, etc.. Collect metadata that is essential and related to the indicator and always remember to pre-test the data collection tool, this can be done through a pilot exercise.
very good lesson and very informative
very good lesson and very informative
Creating data collection tools is a crucial step in monitoring and evaluating projects effectively. It ensures that the necessary information is gathered accurately and efficiently. Let's discuss some key points about creating data collection tools:
Understanding Indicators: Before designing a data collection tool, it's essential to fully understand the indicators being measured. This includes knowing what data needs to be collected, how it will be collected, and how it will be used to measure project success.
User-Centered Design: Consideration should be given to who will be using the data collection tool. Whether it's project staff, volunteers, or participants themselves, the tool should be designed with the end-user in mind. This means keeping the tool simple, easy to understand, and user-friendly.
Focus on Essential Information: Data collection tools should focus on collecting essential information that directly relates to the indicators being measured. Avoid adding unnecessary questions or fields that could complicate the tool and make data collection more difficult.
Incorporating Metadata: Metadata, such as the date, time, location, and person collecting the data, are essential for tracking the context of the collected data. Ensure that the data collection tool includes space to record this metadata alongside the primary data.
Pre-Testing and Revision: Before deploying the data collection tool, it should be thoroughly tested to identify any potential issues or challenges. This can be done through field testing or simulated scenarios. Based on the feedback received during testing, revisions should be made to improve the tool's effectiveness and usability.
Clear Instructions: Providing clear and detailed instructions for using the data collection tool is crucial. This ensures that data collectors understand their roles, know how to complete the tool accurately, and follow standardized procedures.
Continuous Improvement: Data collection tools should be seen as dynamic documents that can be updated and improved over time. Feedback from data collectors and users should be solicited regularly to identify areas for enhancement and optimization.
By following these principles and best practices, organizations can create data collection tools that facilitate the collection of high-quality data, leading to more accurate monitoring and evaluation of projects.
Data are very important in any project implementation. It is important to collect the right data using the right tools and methods in order to eliminate bias and also measure effectively the impact of the project. When creating a data collection tool, considering should be given to the type of data that is to be collected, the population involved, who will be using the tool among other factors.
Setting clear objectives is an essential first step. Establish definite goals by involving pertinent stakeholders and team members in a collaborative, iterative process. To make sure you concentrate your efforts on obtaining the necessary data, it's critical that projects begin with the identification of essential questions and desired results.
Tips for creating data collection tools - Identify who will use the tool, focus on essential information, collect metadata and pre-test your tool and finally prepare staff to use the tool and include instructions.
After you’ve chosen the data collection method that best meets the goals of your registry, it’s time to create the fields that will enable you to gather the information you want from each participant.
Keep these things in mind as you develop the form:
Include a title.
Explain the purpose of the form.
Provide an estimate of time needed to complete the form.
Provide clear instructions.
Ask only for information that’s needed.
Select the appropriate question type (e.g., multiple-choice, drop down menu, checkbox).
Use clear language.
Consider the order of your questions. More important questions are typically found at the beginning of the form.
Creating the Participant Tracking Tool seemed challenging at first but as i progressed along it became interesting , it help me come up with a proper form for my project by ensuring there were no errors, i even got my friend to help test it out
it has helped a great deal
I found this module very useful considering that a good design of your data collection tool will somehow guarantee that you have the right data once you use it, otherwise, the tool might be a waste of time and resources. Adding metadata to the tool is also very relevant since it is very important to keep track of who uses the tool and when. I would add that if the tools are used physically, they should transferred to a digital form later. This is because over time you might need to go back to the tools. Also creating a metadata matrix could be very helpful, so that you can integrate or merge different data bases using one single datum, such as the collection tool name, which will allow you to analyse trends or changes on the data over time.
It is important to review the Participant Tracking Form before it is given or used with the interviewee since there may be problems or changes to be made.
Data collection tools are at the core of project implementation. orientating data collectors on the tools is very important
The creation of data collection tools is a step that should not be underestimated, and requires us to determine and understand the information we wish to collect. We also need to determine the data collection method in order to identify the tools to be used if they already exist or need to be created.
Data collections are tools that help and enable researchers, evaluators and monitoring officers to collect both qualitative and quantitative data. these tools are so essential as they help you gather accurate and non biased data about the people. therefore we should be careful while selecting a method and the tool aswell. consider the population you will be interacting with before designing a tool, go through the tool to ensure realnes and the easeness of the tool.
Creating a data collection tool involves developing a system or method to gather specific information or data from individuals, groups, or systems. This tool can take various forms, such as a questionnaire, survey, application, website form, or any interface designed to capture data accurately and efficiently.
The process of creating a data collection tool typically includes:
Identifying Data Requirements: Understanding the type of data needed, its purpose, and how it will be utilized.
Designing the Tool Interface: Creating the user interface or form for data collection. This entails determining question formats, response types (e.g., multiple-choice, text, numeric), and any validation criteria.
Implementing Validation Measures: Adding checks and constraints to ensure that entered data meets specific criteria (e.g., valid email addresses, numeric values within a defined range).
Ensuring Privacy and Security: Incorporating measures to safeguard the privacy and security of collected data, including encryption, access controls, and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Testing and Quality Assurance: Thoroughly testing the data collection tool to identify and address any issues or bugs, encompassing both functionality and user experience.
Deploying the Tool: Making the data collection tool accessible to users via distribution channels such as email, websites, mobile apps, or physical forms.
Managing Collected Data: Establishing procedures for storing, organizing, and managing collected data effectively, which may involve databases, spreadsheets, or specialized data management systems.
Analyzing Data: Extracting insights and information from collected data through analysis techniques such as statistical analysis, data visualization, or machine learning.
Iterating and Improving: Continuously refining the data collection tool based on feedback, evolving requirements, and insights gained from the collected data.
data collection tools across various categories:
Online Survey Platforms:
SurveyMonkey
Google Forms
Typeform
Qualtrics
Formstack
Offline Survey Solutions:
SurveyCTO
Magpi
KoBoToolbox
Mobile Data Collection Applications:
Fulcrum
iFormBuilder
QuickTapSurvey
Survey123 by Esri
Open Data Kit (ODK)
Web Form Creation Services:
JotForm
Wufoo
Formsite
123FormBuilder
Data Collection Platforms:
Zoho Creator
Airtable
Microsoft PowerApps
Caspio
Data Collection APIs and SDKs:
Google Forms API
Typeform API
SurveyMonkey API
Formstack API
Research-Specific Data Collection Tools:
REDCap
LimeSurvey
Qualtrics (also utilized in academic research)
Market Research Data Collection Solutions:
SurveyGizmo
QuestionPro
Confirmit
Fieldwork Data Collection Tools:
Fulcrum
Magpi
SurveyCTO
KoBoToolbox
Custom Development Frameworks (for building tailored data collection solutions):
Flask (Python)
Django (Python)
Node.js (JavaScript)
React (JavaScript)
Angular (JavaScript)
Some basic elements of a good data collection tool include;
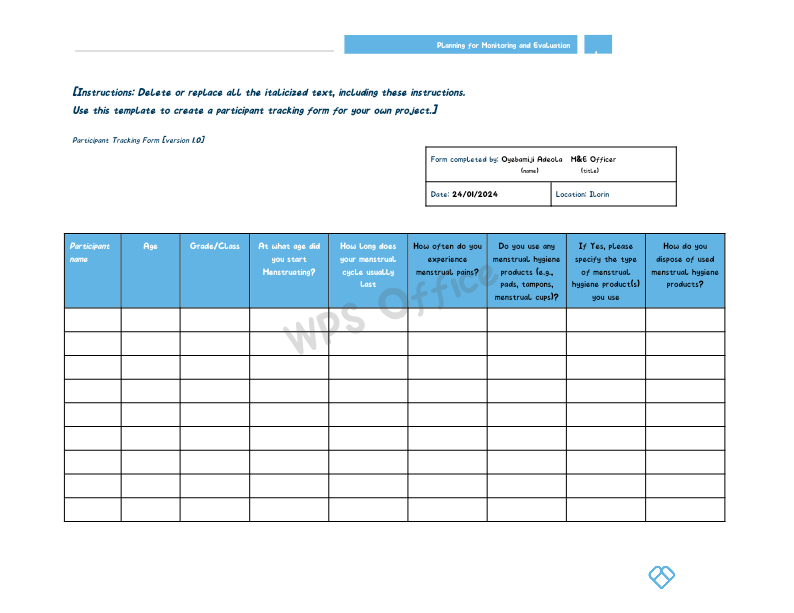
Creating data collection tools is an easy way to get required information from participants. Data collection tools needed to be created in order for the researcher to have a well organized research, for easy collection of information. The easiest example of a creating data collection tools is the Participant Tracking Form.
The tool can be questionnaire survey or interview guide
Data collection tools are forms, documents or guides that help individuals or organizations collect data. When you want to create a data collection tool, its possible to investigate if there exists an appropriate tool that has already been used. This will save you time and resources and also ensures that that the tool you use is high quality.
Then you need to ensure that you use the fewest possible data collection tools by grouping your indicators. A group of indicators can be measured with the same tool if they share the same;
-data collection method
-source
-have the same schedule
Those indicators that cant be grouped are either eliminated or changed to fit with other indicators
You should apply the following tips while creating data collection tools;
-Identify who will use the tool; consider their education, experience with the tool and how comfortable they are using the tool.
-Focus on essential information.
-Collect metadata i.e who collected the data, when the data was collected, where the data was collected, name and version of the tool used.
-Pretest you tool.
-Train your staff to use the tool and indicate the instructions.
It is important to understand test data tools to ascertain errors or areas that require improvement before deploying the form. This will help in ensuring that required data sets are collected accurately and can be analyzed effectively for accurate decision making.
When creating a data collection tool, it is important to focus on essential information/questions to avoid lengthy and confusing tools. grouping indicators in to collections that can be measured with the same tools helps to save on time and resources.
When creating a data collection tool, it is important to focus on essential information/questions to avoid lengthy and confusing tools. grouping indicators in to collections that can be measured with the same tools helps to save on time and resources.
One of the tips of creating data collection tools is focusing on the essential information /questions to avoid lengthy and complicated tool. in addition, group your indicators in to collections that can be measured with the same tool to save on time and resources. This is possible if the indicators share the same data collection method, source and collection frequency/ schedule.
Is a list of participants the same as a participant tracking form
Creating effective data collection tools is essential for gathering accurate and relevant information to support monitoring and evaluation efforts. Here are some steps you can follow to create data collection tools:
Define Objectives and Indicators: Start by clearly defining the objectives of your monitoring and evaluation efforts. What specific information do you need to collect? Identify key indicators that will help you measure progress towards your goals.
Choose Data Collection Methods: Consider the most appropriate data collection methods for your objectives and context. Common methods include surveys, interviews, focus group discussions, observations, document reviews, and existing data sources.
Design Data Collection Instruments: Based on your chosen methods, design the data collection instruments. This could include survey questionnaires, interview guides, observation checklists, or data extraction forms for document reviews.
Keep it Simple and Clear: Ensure that your data collection instruments are easy to understand and use. Avoid using jargon or overly complex language. Keep questions clear, concise, and focused on the information you need.
Use Standardized Formats: Standardize your data collection formats to facilitate analysis and comparison. Use consistent question formats, response options, and coding schemes across all instruments.
Guided by the measurement indicators and hence the amount of either qualitative versus quantitative data needed, we make the mix of data collection methods. When more quantitative data is required, its inevitable to go for surveys (natural resource economics and social science studies) or for experiments (biological sciences) even when they are expensive and require good level of expertise to design the tools, the experiments, collect the data, analyze the data, and so on to produce empirical evidence. To remain on course, this may call for hiring experts as consultants to conduct the assessment, and in some cases reallocate resources from other sub activities. My opinion!
In my view, I would say they are different! This is because the list of participants usually captures the name of participants, location details and contacts. However, this new concept of Participants tracking form not only captures metadata but also some information on prioritized measurement indicators. Thanks team!
Clearly summarized and informative details!
Data collection tool development is very important and we have to be careful. I have had to develop a tool and i was the only person who can use the tools. I did not consider the participants who will be filling the tool, neither did i consider the facilitators who will be supporting and it has been a serious challenge am trying to address and correct now.
Its good to plan the development of the data collection tool with enough documentations and with relevant information in the forms only.
Introducing our new tool for collecting data to help us track and evaluate our projects better. It's easy to use, works offline, gives real-time updates, and keeps our data safe. We'll have training to learn how to use it well. Your feedback will make it even better
Creating data collection tools involves identifying required information, designing clear and concise questions or fields, choosing an appropriate format, pilot testing, training users, and regular updates for accuracy and relevance.
To create data collection tools, define needed information, design clear questions, choose format, pilot test, train users, and update regularly for accuracy.
For data collection tools that will be used over time, it is important that the data be secured (lock box, encrypted/private online database).
When creating data collection tools,is it necessary we go to the field first,